Key Takeaways
- Your URL structure determines how Google understands your site’s country and language targeting.
- The three main options are ccTLDs, subdomains, and subdirectories, each affect rankings, authority sharing, and scalability.
- Hreflang tags tell Google which page to show to users in each region or language.
- Consistent, crawl-friendly URLs prevent duplication and strengthen brand trust.
- A well-planned structure helps Malaysian SMEs expand smoothly into markets like Singapore, Indonesia and Thailand.
URL structure refers to how your web addresses are formatted and segmented to target specific countries or languages. In the context of international SEO, it’s more than just clean links, it’s a signal to search engines about who your content is meant for.
When done right, your URL structure helps Google and other search engines:
- Identify regional targeting
- Avoid duplicate content issues
- Deliver the correct version of a page to users in different locations
- Improve trust and click-through rates (CTR) from users who see a familiar country or language code
Examples of International SEO URL Structures:
yourdomain.my→ Targets Malaysiayourdomain.com/sg/→ Targets Singaporeyourdomain.com/id/→ Targets Indonesia
In each case, the country or language identifier acts as a geo-targeting signal, allowing search engines to rank the right content version for the right audience.
Without a clear structure, your site risks cannibalising its own content in search results especially if different pages serve similar content to different regions. A strong, strategic URL structure supports cleaner indexing, better UX, and higher visibility globally.
Table of Contents
Why URL Structure Matters for Global Visibility
A well-planned URL structure is a core element of international SEO that directly affects how your site ranks and performs across markets.
1. Boosts Local Search Rankings
Google uses URL signals to understand geographical relevance. A proper structure helps your pages appear in local SERPs, especially when combined with hreflang tags, it ensures users see the correct version based on location and language.
2. Improves User Experience
Visitors are more likely to trust and engage with URLs that feel local. A structure like /my/ signals to Malaysian users that they’re in the right place. This clarity reduces bounce rates and supports higher conversion.
3. Builds Regional Trust & Brand Authority
Using country-specific domains like .my or well-structured subdirectories reinforces local presence and trust. For example, a .my domain feels inherently more relevant to Malaysian audiences compared to a generic .com.
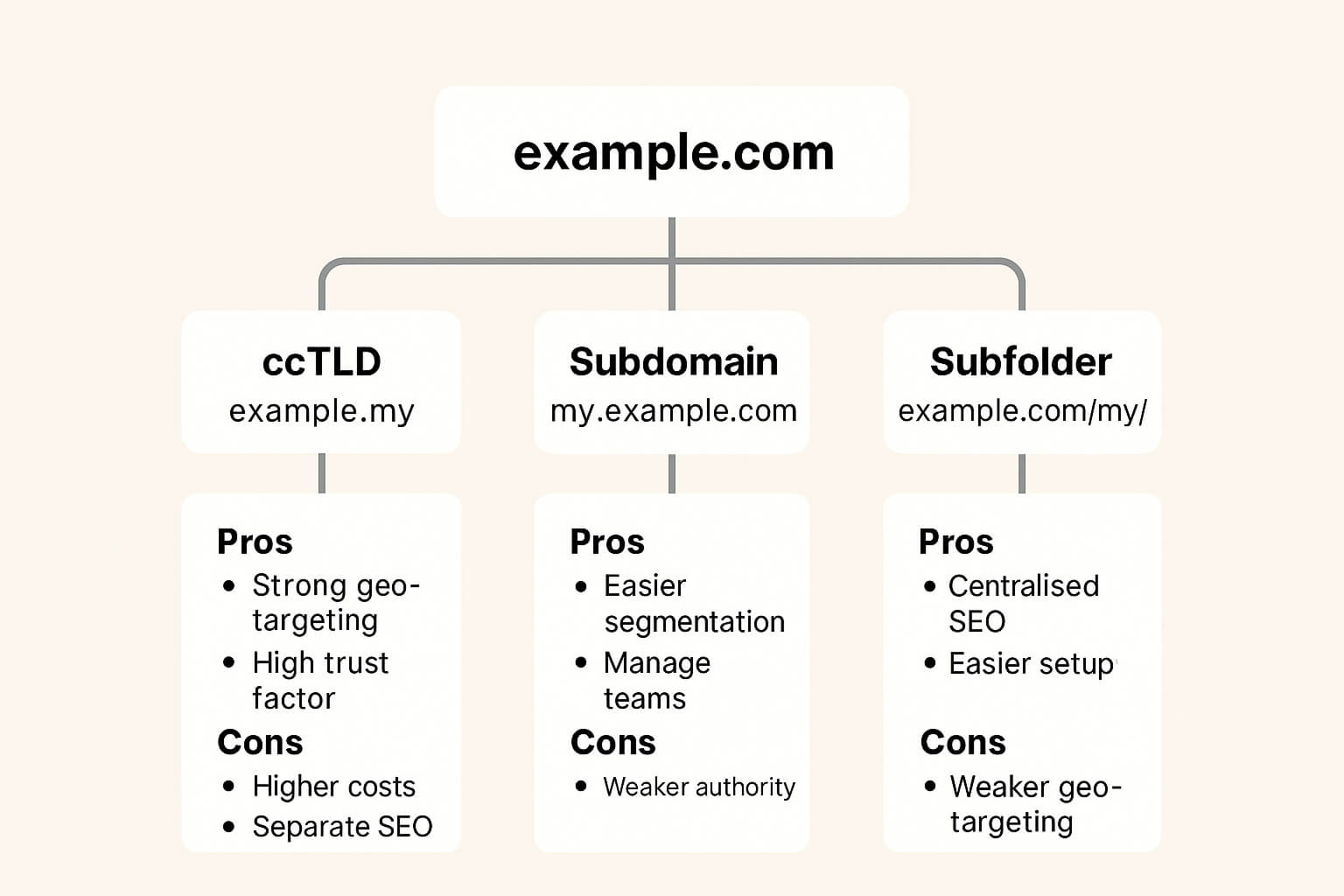
Main Types of International URL Structures
Structure Type | Example | Best For | Advantages | Limitations |
ccTLD (Country Code Top-Level Domain) | domain.my, domain.sg | Businesses focused on a specific country | Clear geo-targeting, high local trust | Higher costs, separate SEO authority per domain |
Subdomain | my.domain.com, sg.domain.com | Multi-region sites needing separation | Easier management per region, can host language variants | Slightly weaker authority sharing than subfolders |
Subdirectory (Subfolder) | domain.com/my/, domain.com/sg/ | SMEs expanding regionally | Centralised SEO value, easier setup | Weaker geo-targeting than ccTLDs |
Which URL Structure Should You Choose?
For Malaysian SMEs:
If you manage a single main website and are expanding into nearby ASEAN markets, subdirectories (domain.com/sg/) are often the most practical option. They:
- Share SEO authority from your primary .com domain
- Are cost-effective and simpler to maintain
- Easily scale across regions, just add /sg/, /id/, /th/, and so on.
For larger enterprises or regulated industries:
ccTLDs (for example example.my, example.sg) are ideal when localisation, legal compliance, or user trust is critical, such as in finance, healthcare, or government sectors. They signal strong regional focus and build confidence with local audiences.
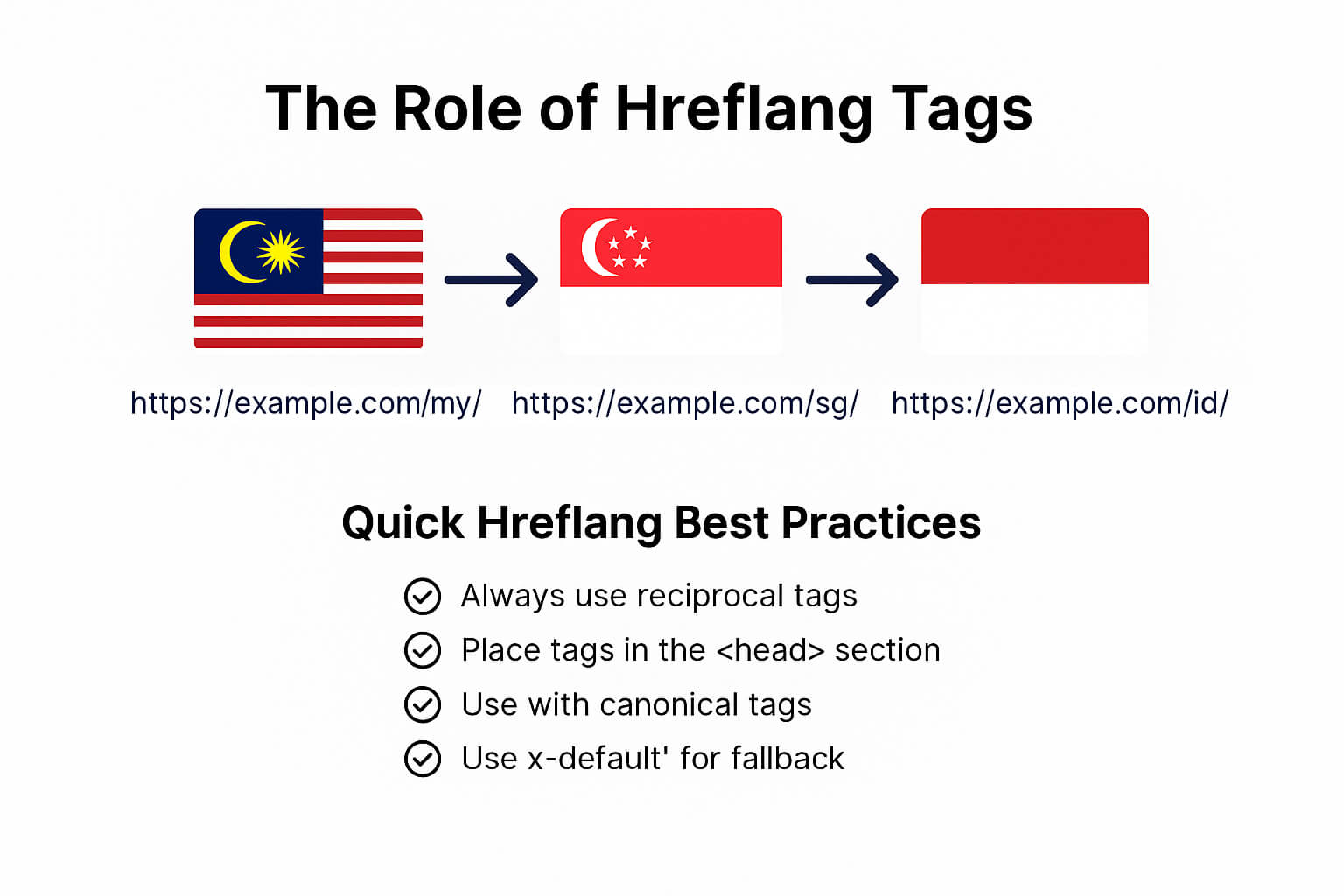
The Role of Hreflang Tags in International SEO
What are Hreflang Tags?
Imagine you own a chain of stores in Malaysia, Singapore, and Indonesia. Each country speaks a different language or version of English. So, you make different versions of your website for each location.
But how does Google know which version to show to which user?
That’s where hreflang tags come in.
Hreflang tags are essential for showing users the correct version of your website based on their language and region. Without them, Google might serve the wrong content. For example, showing your Malaysian audience the Singaporean or global page.
Example:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-my" href="https://domain.com/my/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="id-id" href="https://domain.com/id/" />
These tags act as language-region labels that point search engines to alternate versions of the same content.
Technical SEO Considerations for International URLs
1. Use Canonical Tags to Avoid Duplicate Content
If your site has similar or duplicate pages (like tracking URLs), canonical tags tell Google which version to prioritise for SEO to prevent duplicate content issues and keep your SEO value focused on a single version.
Example:
domain.com/shoes
domain.com/shoes?ref=ad
Add a canonical tag on the second page (duplicate/similar version) to point to the main one:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://domain.com/shoes"/>This ensures Google doesn’t split SEO value across variations.
Read more: Essential HTML Tags for SEO: Canonical, Hreflang & Meta Explained (2025 Guide)
2. Consistent Internal Linking
Link between different country or language versions with clear anchor text like “Visit our Singapore site.” Avoid redirect chains or broken links between regional pages.
3. Geo-Targeting in Google Search Console
If you use subdomains or subfolders (like domain.com/sg/), you can set target countries in Google Search Console’s International Targeting tool.
Common Mistakes in International URL Setup
Mistake | Why It Hurts | How to Fix |
Mixing languages on the same URL | Confuses both users and Google | Separate by language (/en/, /ms/, /zh/) |
Using automatic IP redirection | Google can’t crawl the correct versions | Use hreflang instead of auto-redirects |
Ignoring canonical tags across regions | Creates duplicate content | Set canonicals + hreflang tags together |
Inconsistent URL formats | Hurts crawling, indexing, and analytics | Use a consistent structure across countries |
Optimising URLs for Multilingual SEO
1. Use Language Codes in URL Paths
Add short codes like /en/, /ms/, or /zh/ to clearly indicate the language of the page.
Example: domain.com/ms/perkhidmatan/
2. Use Hyphens, Not Underscores
Google treats hyphens as proper word separators.
✅ domain.com/seo-tips
❌ domain.com/seo_tips
3. Keep URLs Clean and Readable
Avoid long strings of numbers, symbols, or encoded characters.
Bad: domain.com/ms/page?id=123abc
Good: domain.com/ms/panduan-seo
4. Translate URL Slugs Where It Makes Sense
Localise slugs for better user experience and relevance.
Example:
English: /seo-services/
Malay: /perkhidmatan-seo/
Tools for Managing International URL SEO
Tool | Use Case | Notable Features |
Google Search Console | Monitor indexing & hreflang issues | nternational Targeting, Coverage Reports |
Screaming Frog | Crawl multi-language sites | Finds broken links, redirect chains, hreflang errors |
Ahrefs / SEMrush | Track keywords by country | Regional keyword rankings, backlink data |
Hreflang Tags Generator | Automate tag creation | Bulk XML or HTML tag export |
PageSpeed Insights | Test regional page performance | Region-specific Core Web Vitals insights |
How to Maintain a Healthy International URL Framework
- Run monthly audits to check for broken links, redirect chains, or incorrect language-region pairings.
- Create separate XML sitemaps for each country or language version to help search engines crawl and index efficiently.
- Track traffic by region in Google Analytics 4 using geo-reports and language dimensions.
- Document your URL and hreflang structure clearly for developers, marketers, and content teams to avoid inconsistency or conflicts during future expansions.
Conclusion: Build a Scalable International SEO Foundation
The best URL structure for international SEO isn’t one-size-fits-all.
For Malaysian SMEs expanding into ASEAN, subdirectories (with proper hreflang and canonical setup) often offer the best mix of SEO strength and cost-efficiency. Larger enterprises can invest in ccTLDs for maximum local trust and market separation.
If your website is going regional and you want expert help building a scalable, technically sound global SEO framework, Rankpage’s International SEO specialists can guide you through every step from structure planning and hreflang setup to link strategy and analytics.
Legal Disclaimer: All brand names, trademarks, and logos displayed on this website are the intellectual property of their respective owners. Their use herein is solely for identification purposes without written consent or direct affiliation from the respective owner.
Frequently Asked Questions About URL Structure for International SEO
What is the best URL structure for multilingual websites?
Use subdirectories (/en/, /ms/, /zh/) to keep authority centralised while serving different languages.
Should I use country domains or subfolders?
Use country domains (ccTLDs) if you operate separate entities per market, otherwise, subfolders are easier to maintain.
How do hreflang tags help SEO?
They tell Google which version of a page to serve based on language and region, avoiding duplicate-content issues.
Can I target multiple countries with one domain?
Yes, by using subdirectories and hreflang tags for each region.
What happens if I change my URL structure?
Set 301 permanent redirects from old URLs to new ones to preserve SEO value and avoid broken links.
How do I measure international SEO performance?
Track organic traffic and keyword positions by country in Google Search Console and analytics tools.